Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Current issue
Original Articles
- Patterns of self-harm/suicide attempters who visited emergency department over the past 10 years and changes in poisoning as a major method (2011–2020)
- Kyu Hyun Pai, Sung Woo Lee, Su Jin Kim, Kap Su Han, Juhyun Song, Sijin Lee, Ji Hwan Park, Jeijoon Song
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):69-80. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00019

- 486 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Suicide ranks among the top causes of death among youth in South Korea. This study aimed to identify the characteristics of suicidal individuals treated at emergency departments between 2011 and 2020.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted using data from January 2011 to December 2020 in the Injury Surveillance Cohort, a prospective registry. Patients’ sex, age, mortality, methods of self-harm, and previous suicide attempts were analyzed. The methods of self-harm were categorized into falls, asphyxiation, blunt injuries, penetrating injuries, poisoning, and others. Sub-groups with and without poisoning were compared.
Results
The proportion of self-harm/suicide attempts increased from 2.3% (2011) to 5.0% (2020). The mortality rate decreased from 10.8% (2011) to 6.3% (2020). Poisoning was the most common method (61.7%). Mortality rates ranged from 42.0% for asphyxiation to 0.2% for blunt injuries. Individuals in their 20s showed a marked increase in suicide/self-harm attempts, especially in the last three years. A large proportion of decedents in their 70s or older (52.6%) used poisoning as a method of suicide. The percentage of individuals with two or more previous attempts rose from 7.1% (2011) to 19.7% (2020). The death rates by poisoning decreased from 7.7% (2011) to 2.5% (2020).
Conclusion
Our findings underscore the urgent need for targeted interventions and suicide prevention policies. Managing and reducing suicide and self-harm in emergency settings will require a focus on poisoning, the 10–29 age group, and the elderly. This paper will be valuable for future policies aiming to reduce the societal burden of suicide and self-harm.
- Protective effects of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) extract on N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)–induced cellular toxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells
- In Ho Jo, Yoo Ji Kim, Seon Tae Kim
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):81-91. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00021
- 422 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Edible insect extracts have been used as an alternative source for medicinal supplements due to their significant antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activity. Recent studies have reported that anti-microbial peptides from insects have neuroprotective effects on dopamine toxins. The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective functions of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) extract (MWE) on N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)–induced cellular toxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.
Methods
Cellular toxicity induced by the MPTP toxin and the impact of MWE on cell survival were analyzed using MTT assays. DAPI staining was performed to observe apoptotic phenomena caused by MPTP. Changes in caspase-3 activity and protein expression were observed using enzyme activity assays and western blot assays, respectively.
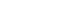
Results
MWE exerted significant antioxidant activity, which was measured by both DPPH and ABTS radical assays, with a dose-dependent relationship. Furthermore, MWE resulted in cellular proliferation in SH-SY5Y cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, MWE pretreatment significantly inhibited MPTP-induced cytotoxicity, with a dose-dependent relationship. The morphological characteristics of apoptosis and increased reactive oxygen species induced by MPTP were also significantly reduced by MWE pretreatment.
Conclusion
MWE treatment significantly attenuated MPTP-induced changes in the levels of proteins associated with apoptosis, such as caspase-3 and PARP. These findings suggest that MWE exerts neuroprotective effects on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells subject to MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration.
- Demographic characteristics of patients admitted to the emergency department for intoxication and a time series analysis during the COVID-19 period
- Bongmin Son, Nayoon Kang, Eunah Han, Gina Yu, Junho Cho, Jaiwoog Ko, Taeyoung Kong, Sung Phil Chung, Minhong Choa
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):92-107. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00011
- 434 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: This study investigated the characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients who visited the emergency department due to intoxication and analyzed the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on their visits.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted using data from the National Emergency Department Information System (NEDIS) on patients who visited the emergency department due to intoxication between January 2014 and December 2020. In total, 277,791 patients were included in the study, and their demographic and clinical data were analyzed. A model was created from 2014 to 2019 and applied to 2020 (i.e., during the COVID-19 pandemic) to conduct a time series analysis distinguishing between unexpected accidents and suicide/self-harm among patients who visited the emergency department.
Results
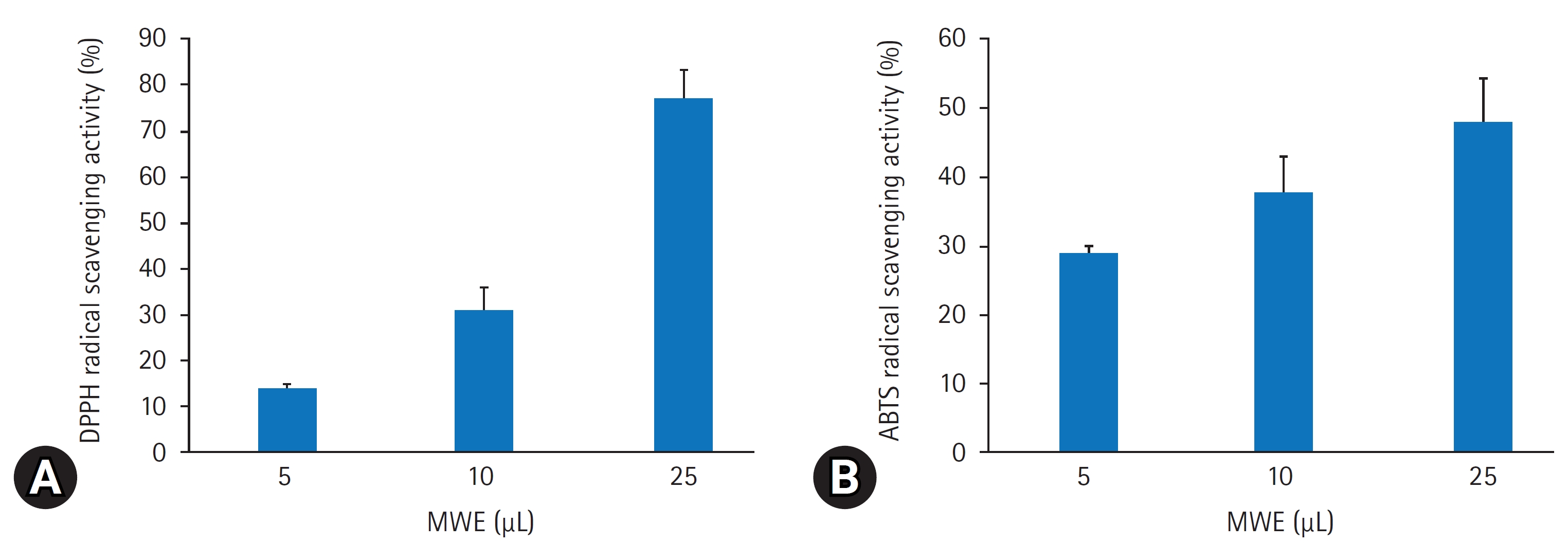
The most common reason for visiting the emergency department was unintentional accidents (48.5%), followed by self-harm/suicide attempts (43.8%). Unexpected accident patients and self-harm/suicide patients showed statistically significant differences in terms of sex, age group, hospitalization rate, and mortality rate. The time series analysis showed a decrease in patients with unexpected accidents during the COVID-19 pandemic, but no change in patients with suicide/self-harm.
Conclusion
Depending on the intentionality of the intoxication, significant differences were found in the age group, the substance of intoxication, and the mortality rate. Therefore, future analyses of patients with intoxication should be stratified according to intentionality. In addition, the time series analysis of intentional self-harm/suicide did not show a decrease in 2010 in the number of patients, whereas a decrease was found for unintentional accidents.
- Changes in the characteristics of acute carbon monoxide poisoning patients who visited the emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jun bo Sim, Tae kyu Ahn, Hyun Kim
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):108-116. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00008
- 718 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: This study investigated the differences between patients with acute carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning who visited the emergency department (ED) before and during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods
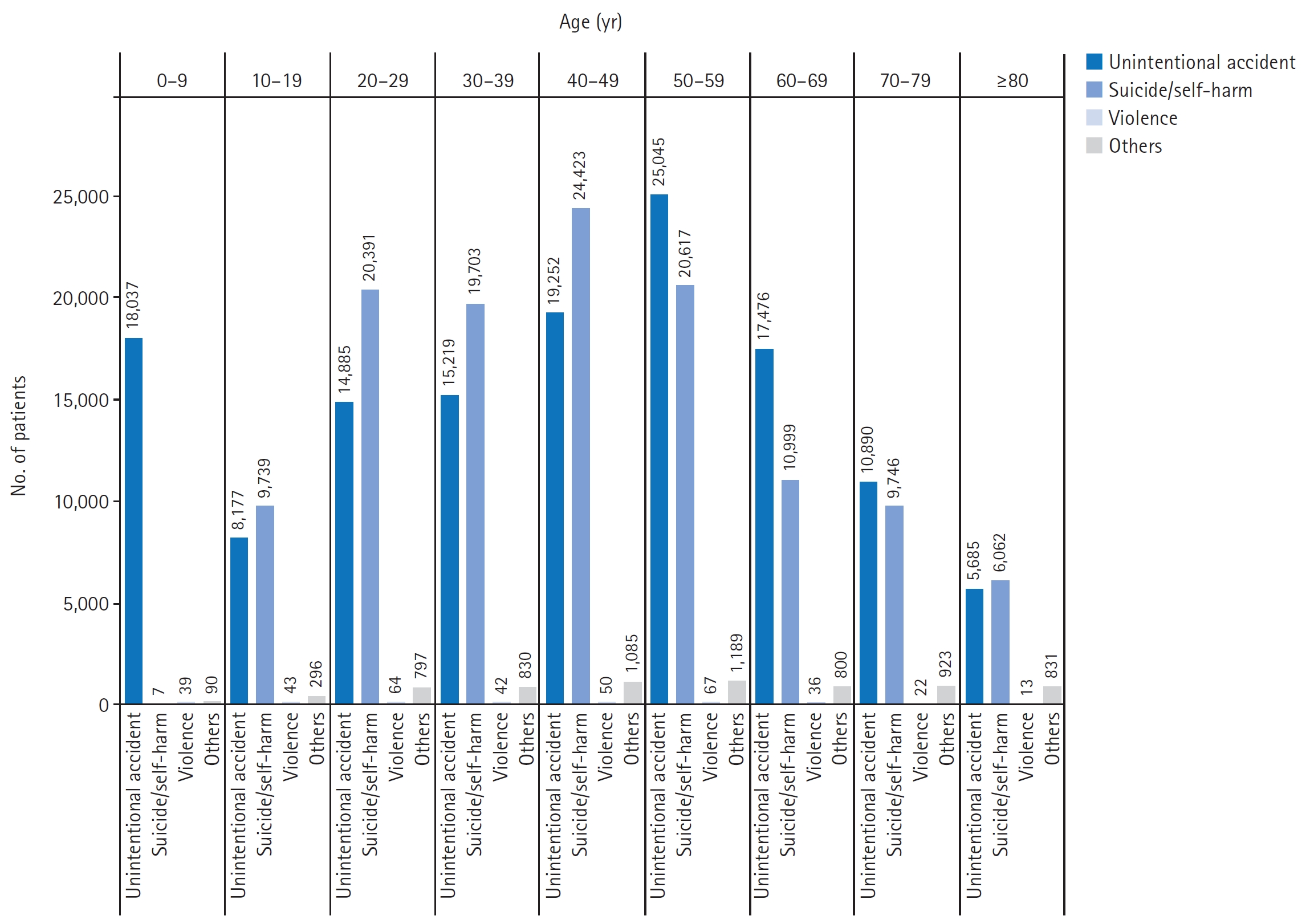
This was a single-center retrospective observational study. Patients with CO poisoning who visited the ED during the period from February 2020 to January 2023 were classified as the COVID-19 pandemic group, and those from February 2019 to January 2020 were classified as the non-pandemic group. Patients’ medical records were reviewed, their demographic and clinical characteristics were compared, and the length of stay in ED was checked. The time from admission to the ED to the start of hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO) was defined as the door-to-HBO time, and this parameter was compared between both groups.
Results
In total, 672 patients were included in this study. The proportion of intentional poisoning was significantly higher in the COVID-19 pandemic group than in the non-pandemic group (p =0.028). The proportion of intentional poisoning significantly increased in the 20- to 29-year-old age group during the COVID-19 pandemic (p <0.001). In addition, it took longer to initiate HBO in the COVID-19 pandemic group than in the non-pandemic group (p =0.001).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that pandemics of infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, increase the proportion of intentional CO poisoning, and it may take longer to initiate HBO after visiting the ED. Efforts will be needed to decrease intentional CO poisoning and length of stay in ED.
- Comparison of hyperbaric oxygen therapy pressures for acute carbon monoxide poisoning
- Jeong Yun Kim, Jihye Lim, Sung Hwa Kim, Sang Il Han, Yong Sung Cha
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):117-127. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00012
- 429 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
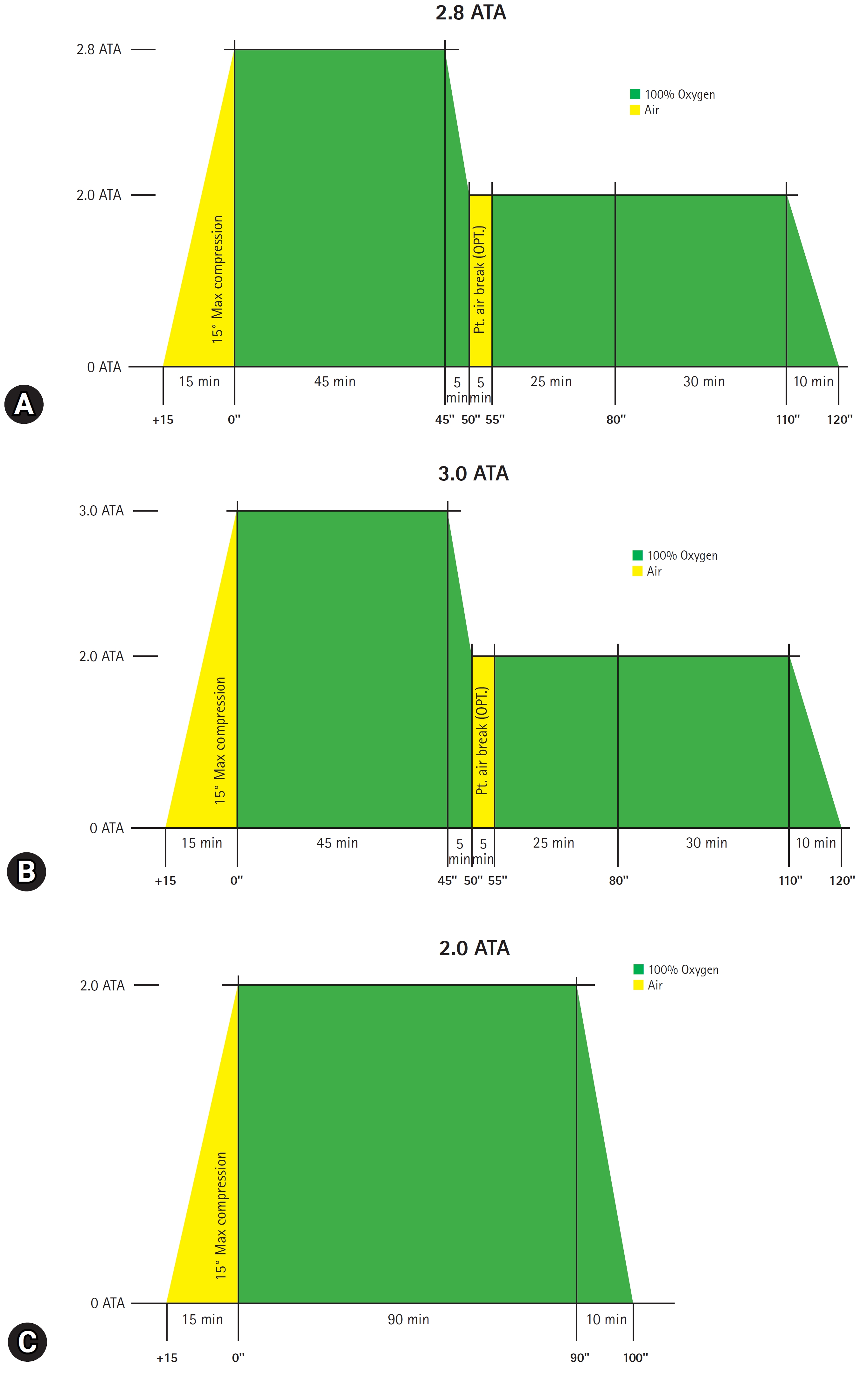
PDF - Purpose: No consensus currently exists regarding the maximal pressure of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO2) therapy performed within 24 hours of acute carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. This study aimed to evaluate the difference in therapeutic effects according to the first HBO2 pressure (3.0 atmospheres absolute [ATA] vs. 2.8 ATA).
Methods
We used prospectively collected registry data on CO poisoning at a tertiary academic hospital in the Republic of Korea. Adult patients with acute CO poisoning treated with HBO2 within 24 hours after arrival at the emergency department and without the use of additional HBO2 after 24 hours between January 2007 and February 2022 were included. Data from 595 patients were analyzed using propensity score matching (PSM). Patients with mild (non-intubated) and severe (intubated) poisoning were also compared. Neurocognitive outcomes at 1 month after CO poisoning were evaluated using the Global Deterioration Scale combined with neurological impairment.
Results
After PSM, the neurocognitive outcomes at 1-month post-CO exposure were not significantly different between the 2.8 ATA (110 patients) and 3.0 ATA (55 patients) groups (p=1.000). Similarly, there was also no significant difference in outcomes in a subgroup analysis according to poisoning severity in matched patients (165 patients) (mild [non-intubated]: p=0.053; severe [intubated]: p=1.000).
Conclusion
Neurocognitive sequelae at 1 month were not significantly different between HBO2 therapy pressures of 2.8 ATA and 3.0 ATA in patients with acute CO poisoning. In addition, the 1-month neurocognitive sequelae did not differ significantly between intubated and non-intubated patients.
- Predicting serum acetaminophen concentrations in acute poisoning for safe termination of N-acetylcysteine in a resource-limited environment
- Dahae Kim, Kyungman Cha, Byung Hak So
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):128-134. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00013
- 461 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
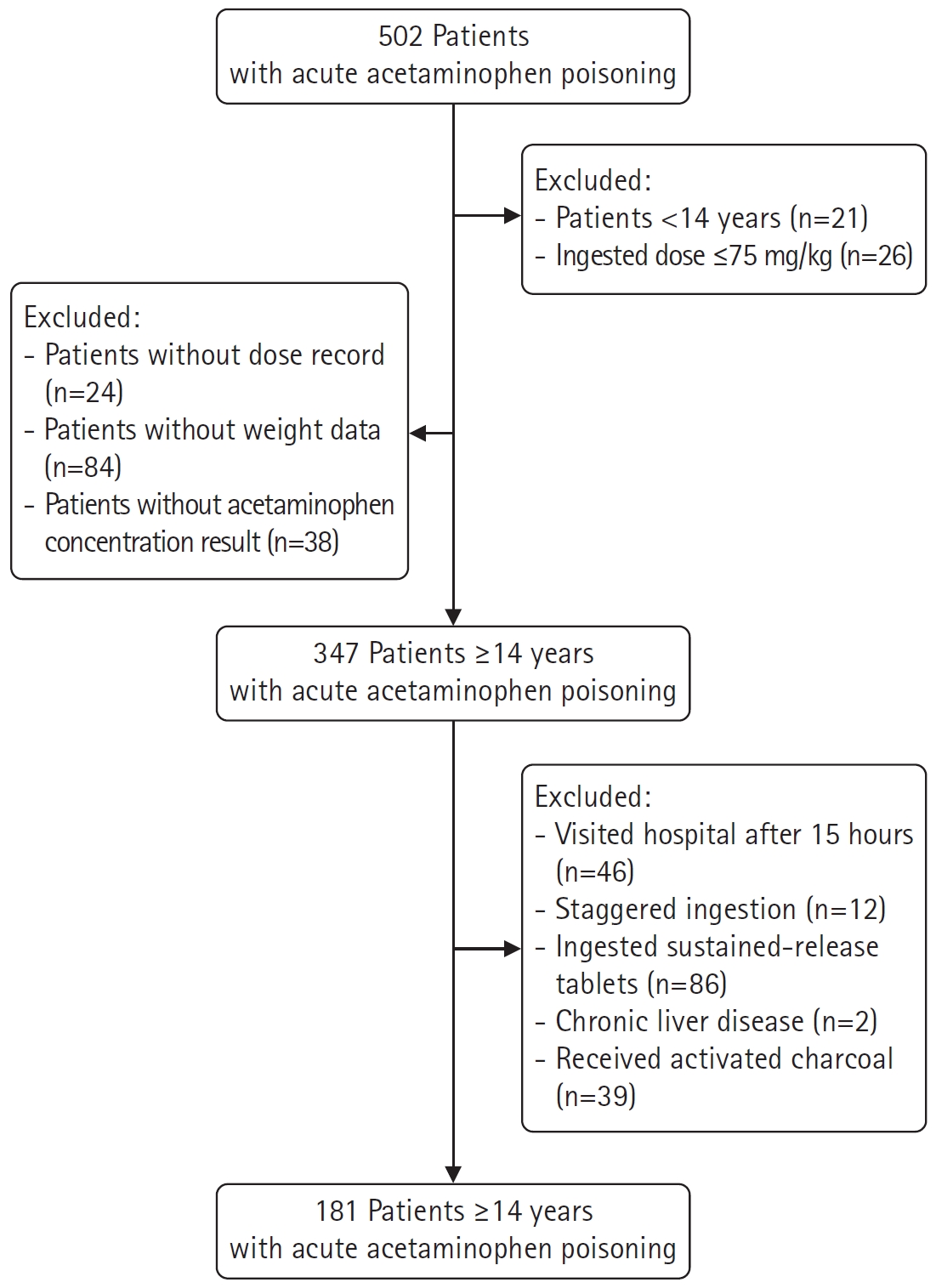
PDF - Purpose: The Prescott nomogram has been utilized to forecast hepatotoxicity from acute acetaminophen poisoning. In developing countries, emergency medical centers lack the resources to report acetaminophen concentrations; thus, the commencement and cessation of treatment are based on the reported dose. This study investigated risk factors that can predict acetaminophen detection after 15 hours for safe treatment termination.
Methods
Data were collected from an urban emergency medical center from 2010 to 2020. The study included patients ≥14 years of age with acute acetaminophen poisoning within 15 hours. The correlation between risk factors and detection of acetaminophen 15 hours after ingestion was evaluated using logistic regression, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated.
Results
In total, 181 patients were included in the primary analysis; the median dose was 150.9 mg/kg and 35 patients (19.3%) had acetaminophen detected 15 hours after ingestion. The dose per weight and the time to visit were significant predictors for acetaminophen detection after 15 hours (odds ratio, 1.020 and 1.030, respectively). The AUCs were 0.628 for a 135 mg/kg cut-off value and 0.658 for a cut-off 450 minutes, and that of the combined model was 0.714 (sensitivity: 45.7%, specificity: 91.8%).
Conclusion
Where acetaminophen concentrations are not reported during treatment following the UK guidelines, it is safe to start N-acetylcysteine immediately for patients who are ≥14 years old, visit within 15 hours after acute poisoning, and report having ingested ≥135 mg/kg. Additional N-acetylcysteine doses should be considered for patients visiting after 8 hours.
- Utility of the APACHE II score as a neurological prognostic factor for glufosinate-intoxicated patients with alert mental status
- Rok Lee, Tae Yong Shin, Hyung Jun Moon, Hyun Jung Lee, Dongkil Jeong, Dongwook Lee, Sun In Hong, Hyun Joon Kim
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):135-142. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00018
- 536 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: In patients with glufosinate poisoning, severe neurological symptoms may be closely related to a poor prognosis, but their appearance may be delayed. Therefore, this study aimed to determine whether the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score could predict the neurological prognosis in patients with glufosinate poisoning who present to the emergency room with alert mental status.
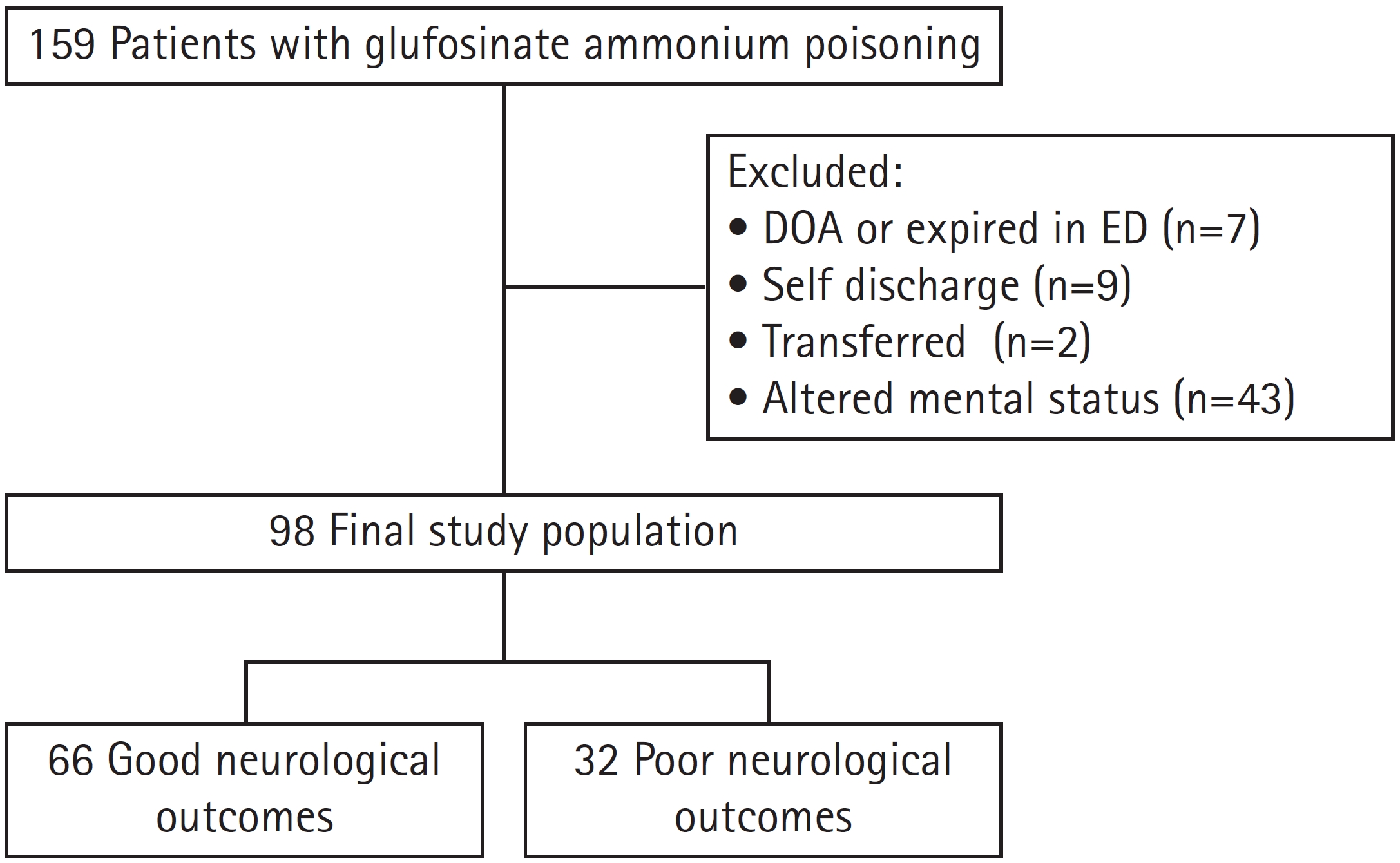
Methods
This study was conducted retrospectively through a chart review for patients over 18 years who presented to a single emergency medical center from January 2018 to December 2022 due to glufosinate poisoning. Patients were divided into groups with a good neurological prognosis (Cerebral Performance Category [CPC] Scale 1 or 2) and a poor prognosis (CPC Scale 3, 4, or 5) to identify whether any variables showed significant differences between the two groups.
Results
There were 66 patients (67.3%) with good neurological prognoses and 32 (32.8%) with poor prognoses. In the multivariate logistic analysis, the APACHE II score, serum amylase, and co-ingestion of alcohol showed significant results, with odds ratios of 1.387 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.027–1.844), 1.017 (95% CI, 1.002–1.032), and 0.196 (95% CI, 0.040–0.948), respectively. With an APACHE II score cutoff of 6.5, the AUC was 0.826 (95% CI, 0.746–0.912). The cutoff of serum amylase was 75.5 U/L, with an AUC was 0.761 (95% CI, 0.652–0.844), and the AUC of no co-ingestion with alcohol was 0.629 (95% CI, 0.527–0.722).
Conclusion
The APACHE II score could be a useful indicator for predicting the neurological prognosis of patients with glufosinate poisoning who have alert mental status.
- A retrospective analysis of toxic alcohol poisoning
- Jin Kim, Yu Jin Lee, Tae Kyu Ahn, Soo Kang
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):143-150. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00014
- 434 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: This study aimed to compare the clinical features of methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning.
Methods
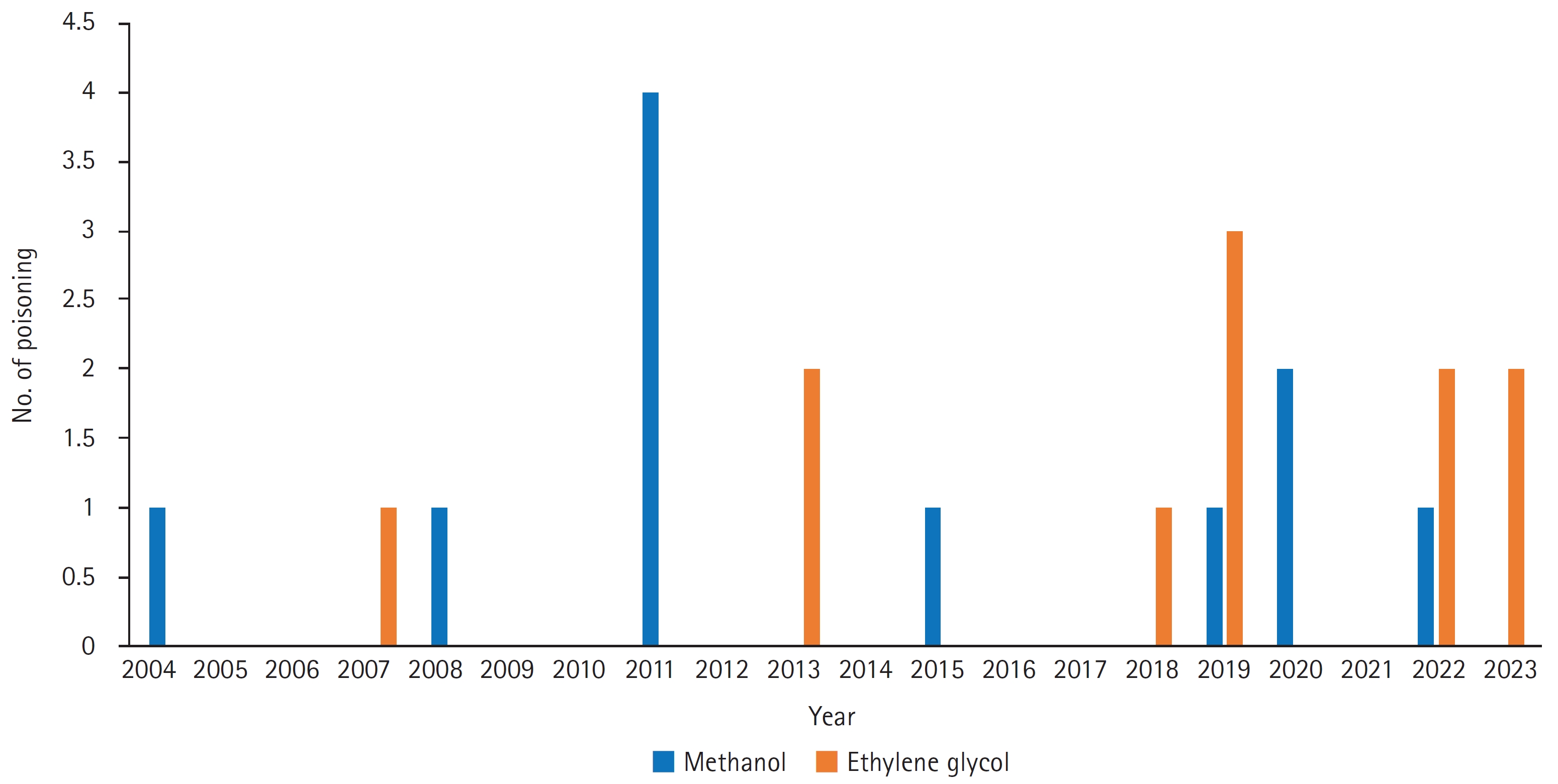
This single-center retrospective observational study included patients with toxic alcohol poisoning who visited a regional emergency medical center. Patients with methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning from January 2004 to June 2023 were selected for the study using diagnostic codes.
Results
Twenty-two patients with toxic alcohol poisoning visited during the study period, with 11 patients for each category. Compared to methanol poisoning, ethylene glycol poisoning patients were more likely to have consumed alcohol for suicidal purposes (n=4 [36.36%] vs. n=8 [72.73%]) and were more likely to be drowsy (n=0 vs. n=6 [54.55%],p =0.016). The anion gap (25.43±8.35 mmol/L vs. 13.22±6.23 mmol/L,p =0.001) and lactic acid levels (1.785 [1.3–2.785] mmol/L vs. 9.90 [4.20–11.81] mmol/L,p =0.007) were higher in ethylene glycol poisoning patients than in methanol poisoning patients. Among alcohol dehydrogenase blockers, oral ethanol was administered to 10 patients (45.45%) (n=4 [36.36%] vs. n=6 [54.55%]), and intravenous ethanol was administered to six patients (n=4 [36.36%] vs. n=2 [18.18%]). Fomepizole was administered to two patients (9.09%) each, and renal replacement therapy was non-significantly more common in patients with ethylene glycol poisoning (n=8 [72.73%] vs. n=3 [27.27%],p =0.128). Three patients had delays in diagnosis and treatment, and while there were no fatalities, one patient was left with permanent vision damage.
Conclusion
Because these are uncommon types of poisoning and the clinical presentation is difficult to recognize early, healthcare providers should be familiar with toxic alcohol types and screen for them to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Case Report
- A case of chronic licorice intoxication-induced apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome
- Young Jae Lim, Ji Eun Kim
- J Korean Soc Clin Toxicol. 2023;21(2):151-155. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22537/jksct.2023.00020
- 441 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
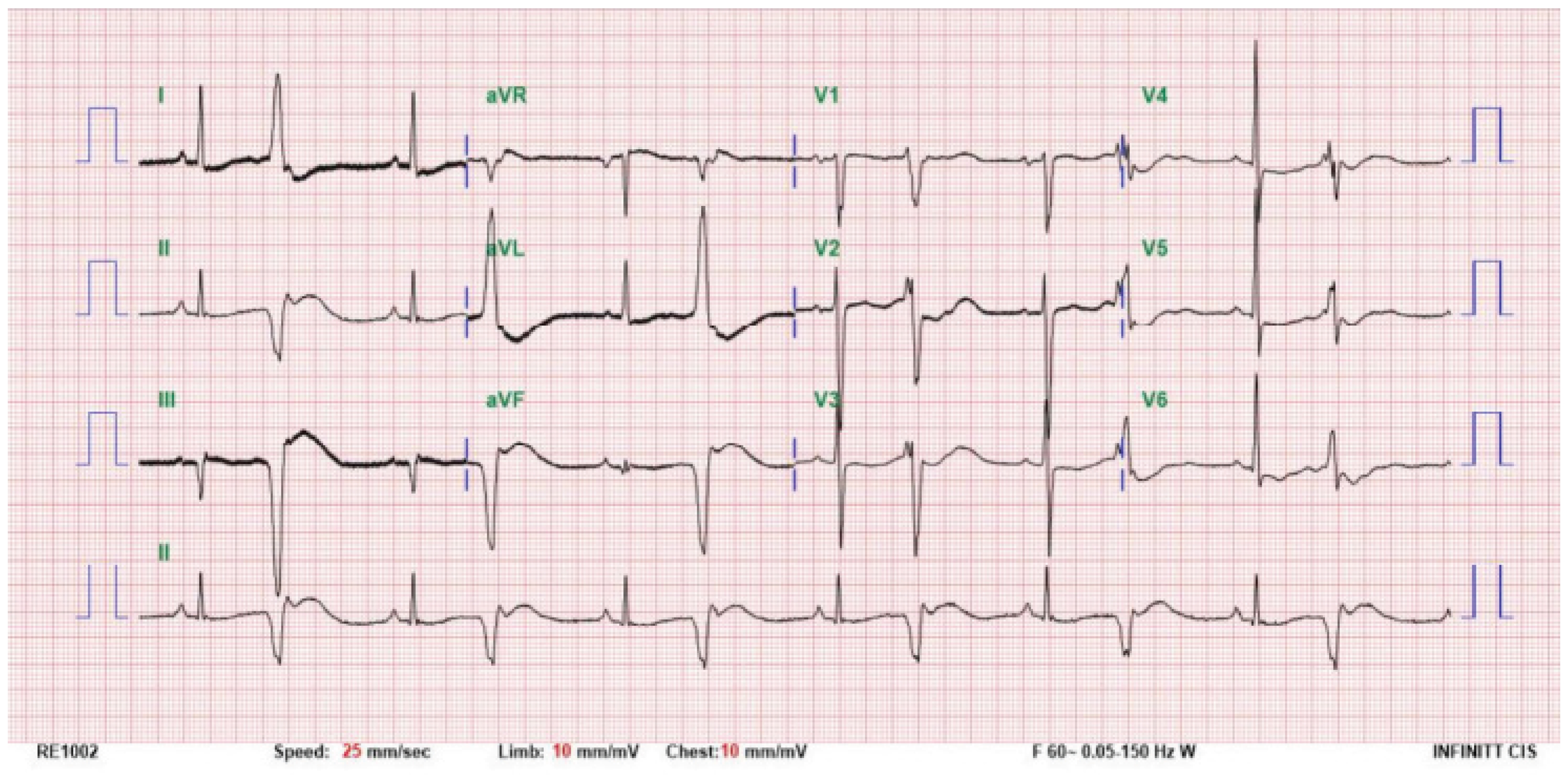
PDF - Licorice is a perennial herb belonging to the legume family that mainly grows in northeastern China, Mongolia, Siberia, and other regions. It is used in traditional medicine in the form of dried roots in the East and the West. The main active component of licorice, glycyrrhizin, is known to produce mineralocorticoid effects when consumed chronically, which can lead to apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome. Herein, we present the case of a 72-year-old woman who was admitted to the emergency room with severe generalized weakness and difficulty keeping her neck upright, which had developed after daily consumption of licorice-infused water for the past 2 months. Blood tests revealed metabolic alkalosis and severe hypokalemia, and an electrocardiogram showed ventricular bigeminy. The patient was treated with daily potassium and spironolactone supplements, leading to a significant improvement in muscle strength after a week. One week later, the patient was discharged, showing rare ventricular premature contractions on electrocardiography, but with no specific complaints. Chronic licorice ingestion leading to hypokalemia and muscle weakness can be life-threatening, necessitating the discontinuation of the causative agent, close monitoring, and cautious supplementation of potassium and spironolactone as treatment.

 KSCT
KSCT


 First
First Prev
Prev



 Korean Society of Clinical Toxicology
Korean Society of Clinical Toxicology